Using a new generation of deep cooling CCD camera, dark current 0.0001e/p/s@-90℃, cooling speed is faster and life is longer;
The f0.7 super lens greatly increases the amount of light entering per unit time, thereby effectively shortening the exposure time, and is especially suitable for bioluminescence imaging of Luc reporter gene detection
Fluorescence imaging uses double-sided high-intensity pulsed LED array scanning light source, multi-channel, and the excitation intensity is higher than that of halogen lamps. Based on scanning mode, excitation uniformity ≥99%;
10-bit emission filter wheel, equipped with 9 dedicated narrow-wave filters to meet the detection needs of various dyes;
Covers the spectral separation function, through multiple scanning of multiple different wavelength lasers, spectral splitting;
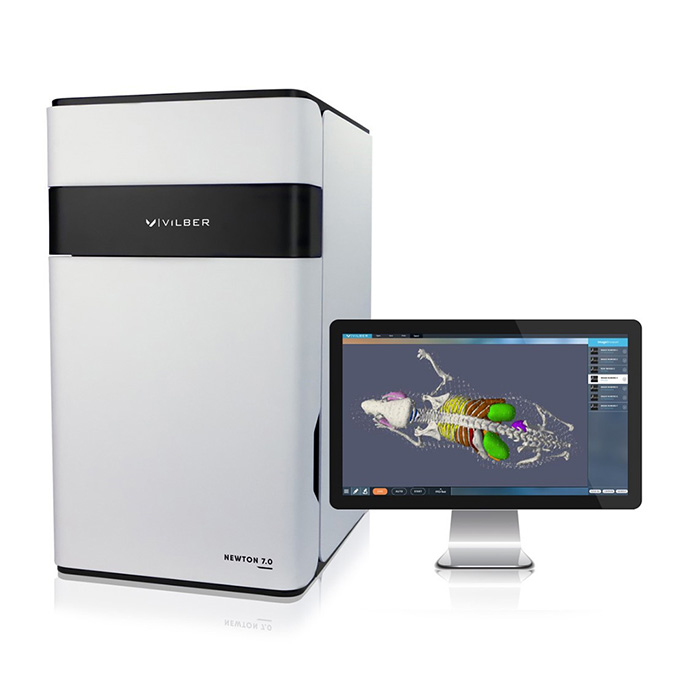
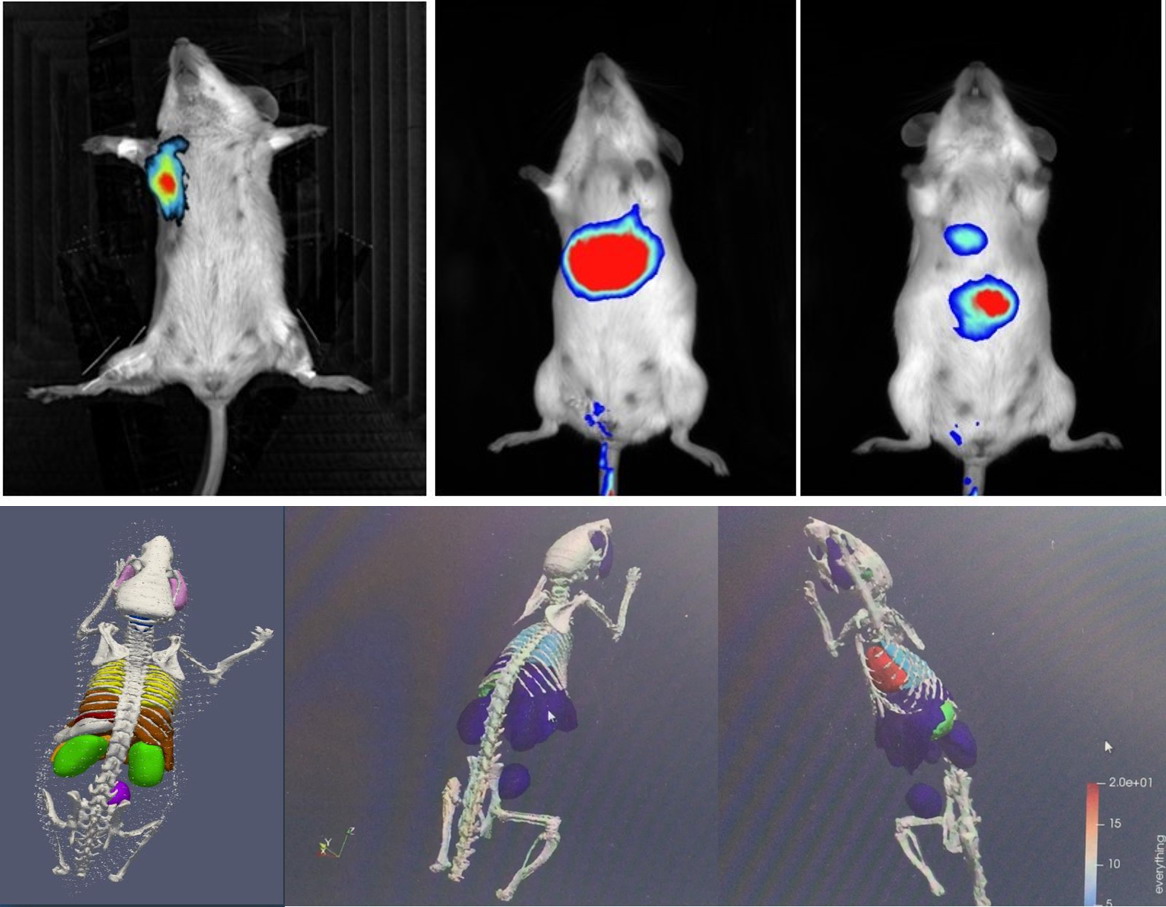
With topology and tomography technology, it realizes optical three-dimensional imaging and accurately locates the signal source;
It has a CCD camera that can be raised and lowered, and a stage that can move along the X and Y axes to achieve three-dimensional control, especially to meet the needs of local imaging of mice and obtain more details;
Equipped with special thermostat for mice, compatible with mouse anesthesia system, the maximum flux can reach 5 mice.
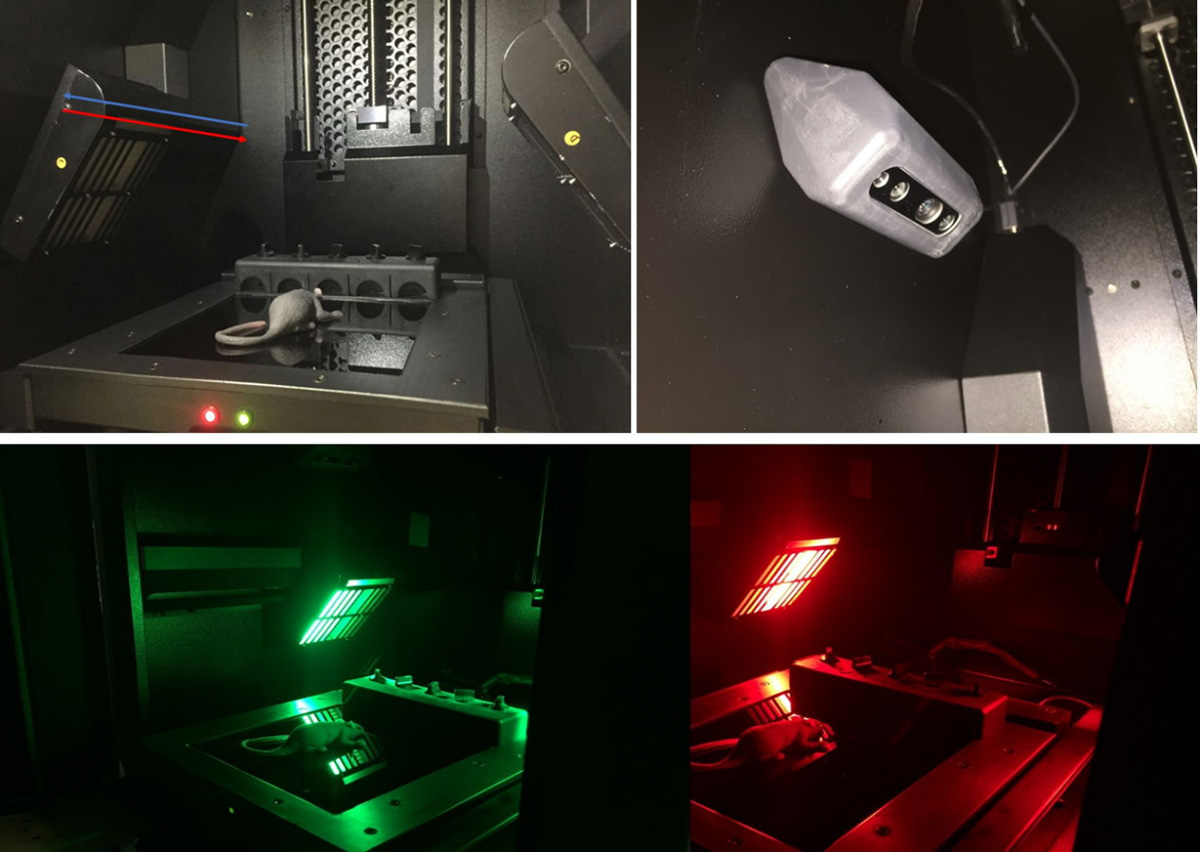

Figure 1.Newton 7.0 FT-500 double-sided array scanning light source
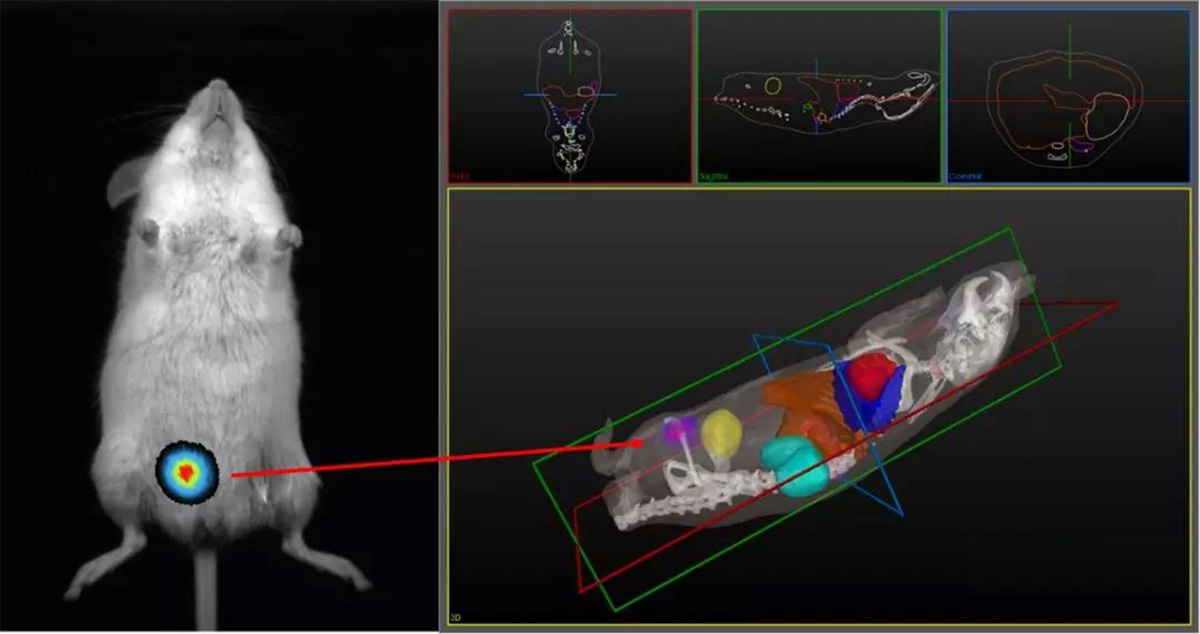
Figure 2. Newton 7.0 FT-500 topology and tomography technology to achieve optical 3D imaging and accurate positioning of the signal source

Figure 3. Newton 7.0 FT-500 spectral separation function, splitting the target fluorescence signal from autofluorescence
It can be used for fluorescence and bioluminescence imaging in mice, cell migration tracking in vivo or in vitro, can be superimposed on signals, and can display multiple reporter genes at the same time. Related molecular mechanism research. Can meet GFP, YFP, Pro -Q Emerald 300, Sypro-Ruby, FITC, DAPI, Alexa Fluor680, 700, 750, Cy3, Cy5, Cy5.5, Cy7, mCherry and other fluorescent dyes.
CCD camera
CCD camera: a new generation of deep refrigeration scientific research level 0 CCD camera @ -90 ℃, 0 defects
Sensitive range: 400 ~ 900nm
CCD dark current: ≤0.0001e / p / s, read noise ≤2e / p / s
Optical lens: V.070 electric control, aperture value ≤0.70, increase the amount of light entering per unit time, especially suitable for bioluminescence imaging
Fully closed camera
Black box: Fully automatic control, the camera can be moved up and down along the Z axis, and the stage can be moved along the X and Y axes to achieve three-dimensional adjustment
Excitation light source: pulsed LED light source, covering the deep blue to near infrared band, each wavelength contains two independent excitation light sources (selectable scanning or non-scanning excitation mode)
Light source life: LED has long service life, 5000 hours guarantee more than 90% output
Filter wheel: 10-bit emission filter wheel, dual magnetron sputtering filter, applicable spectrum range: 400 ~ 900nm
Anesthesia & Respiratory Device
Anesthesia system: compatible with mouse anesthesia system, used for anesthesia of laboratory animals
Breathing device: animal breathing device can choose single interface, three interfaces and five interfaces, up to 5 mice can be simultaneously anesthetized or a single interface for rat anesthesia
Exhaust gas recovery: loaded with high-quality adsorbent ≥1kg, can absorb ≥200g isoflurane
Temperature control device: the temperature control table of the mouse, which controls the constant temperature for a long time to avoid the temperature loss of the mouse under the anesthesia state of the mouse.
Acquisition & Analysis Software
APPS STUDIO function, covering more than 40 experimental methods, and containing the relevant excitation and emission information of various dyes or fluorescent probes, including: GFP, YFP, Pro-Q Emerald 300, Sypro-Ruby, FITC, DAPI, Alexa Fluor680, 700, 750, Cy3, Cy5, Cy5.5, etc.
With fluorescence, bioluminescence, chemiluminescence 2D / 3D functions, it can randomly obtain 2D / 3D graphics to intuitively understand the location of the signal source
With a variety of camera modes, the continuous shooting function can realize the superposition of signals, especially suitable for weak signal samples
The method-driven program can be automatically called, without repeatedly adjusting the camera program, to achieve automatic imaging;
Quantitative analysis function to obtain signal intensity, area and other related values