【Science Advances】MTHI inhibitor amplifies the lethality of reactive oxygen species to tumor in photodynamic therapy

Recently, the team of Zhao Lingzhi and Peng Juanjuan from the School of Basic Medicine and Clinical Pharmacy of China Pharmaceutical University published the latest research results in the journal Science Advances (impact factor 12.804) published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS)-MTH1 Inhibitor Amplifies the Lethality of Reactive Oxygen Species to Tumor in Photodynamic Therapy. The first communication unit is China Pharmaceutical University. Researcher and PhD student Li Junyao of China Pharmaceutical University is the co-first author of this article. Researcher Zhao Lingzhi and Researcher Peng Juanjuan and Professor Yanli Zhao of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore are co-corresponding authors.
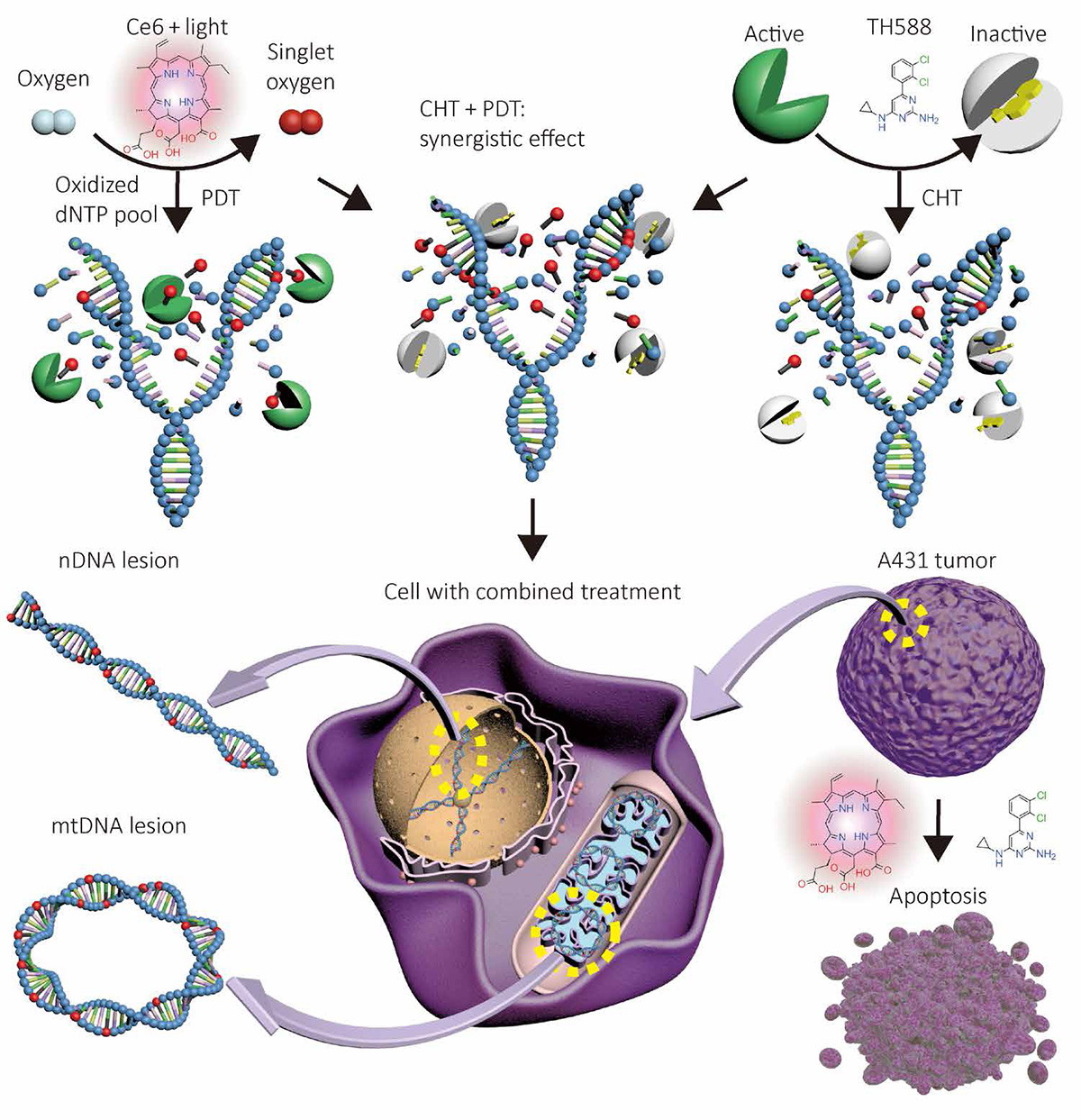
In this study, the small molecule inhibitor TH588 of MTH1 was used as a chemotherapeutic drug, and the photosensitizer Ce6 was co-loaded in nanocarriers to implement a combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT). Through the synergy of the two, a better therapeutic effect is obtained in hypoxic solid tumors. The combination of MTH1 inhibitors and PDT for tumor therapy is not a simple stacking of different treatment methods, but an organic combination of the advantages of the two. TH588 inhibits the defense ability of cancer cells against ROS, and the large amount of ROS generated in PDT can induce apoptosis more efficiently, thereby exerting a synergistic effect, and even better effects can be obtained in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. This research result improves the efficacy of photodynamic therapy and provides new ideas for designing a combined cancer treatment.
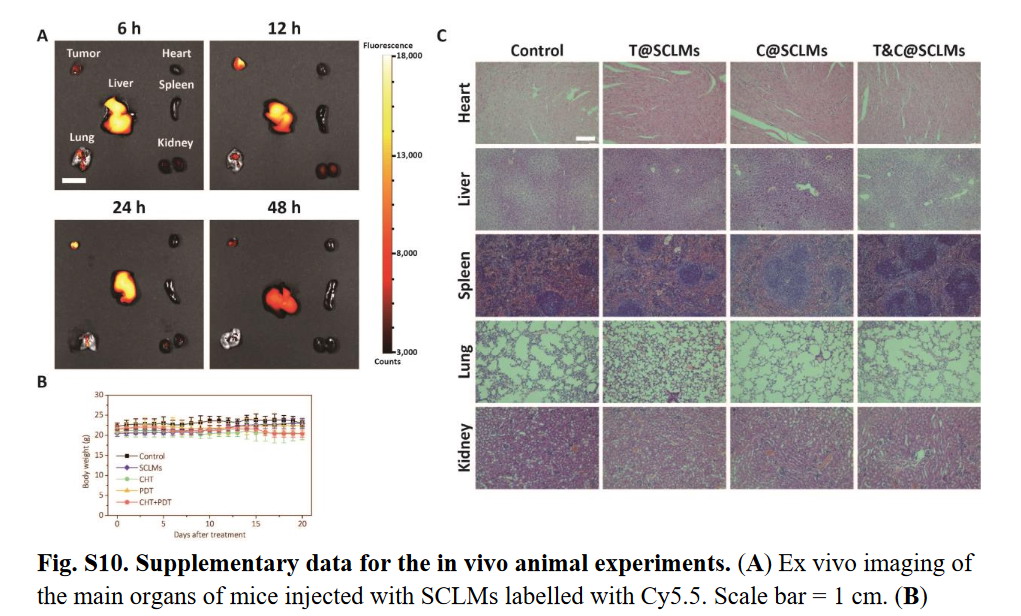
In related experiments, the distribution of Cy5.5 dye-labeled nanocarriers (SCLMs) in mouse tumors and various organs was determined by Fusion FX7, Vilber ’s multifunctional in vivo imaging system (Spectra Capsule NIR680, ex = 680 nm, em = 750 ± 10 nm).